Causes of Social Anxiety Disorder (SAD) - Symptoms, Prevention, Treatment
Anxiety and nervousness is a normal part of everyday life. Some anxiety is a survival mechanism designed to generate concentration and alertness so that we perform at our best and meet your expectations. However, for a surprisingly large proportion of people, stress, fear and anxiety become magnified so that they freeze, become paralysed and feel unable to cope with the situation or all the pressure.
People suffering from Social Anxiety Disorder (SAD) fear social occasions and events where they might be judged or embarrassed. Sufferers experience a variety of symptoms such as trembling, a pounding or racing heart, blushing or sweating.
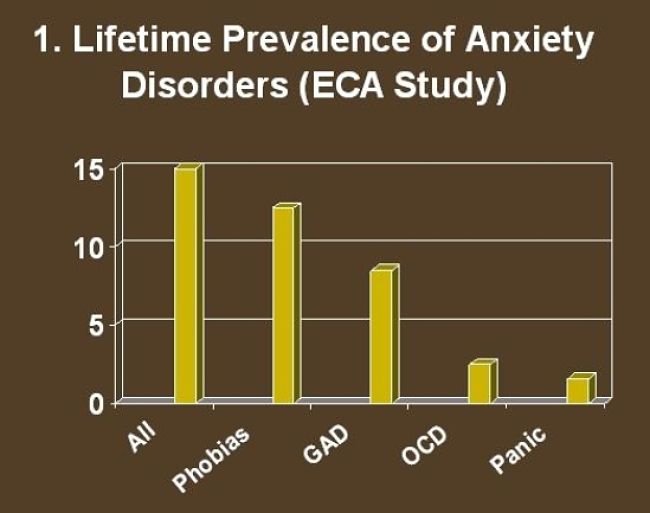
Anxiety disorder is quite common and there are a number of different types such as obsessive compulsive disorder, generalized anxiety disorder, post traumatic stress disorder, specific phobias, but this article focuses on social anxiety disorder in particular, which is the most common type of anxiety disorders.

Types of social anxiety disorder?
People diagnosed with Social Anxiety Disorder can be classified as having:
- A specific disorder applies when a specific situations or event cause social anxiety.
- A generalized social anxiety disorder applies to a range of situations and typically involves a general persistent, recurring and chronic fear of being assessed by others as falling short or being inadequate in some way or being exposed to the risk being embarrassed or humiliated by their own actions or short-comings. These fears can be triggered or thought to be about to occur, through the imagined, perceived or actual scrutiny by others.
Nearly 13 percent of the general population (one in 8) experience some symptoms of social anxiety disorder at least one in their lives. It is more common in females but males are less likely to seek treatment or relief. Most sufferers are aware of and recognize their fear of social phobias as being unreasonable or excessive. However research has shown that social phobias are very hard to overcome, even when people seek help and many people live their lives with social interaction disabilities which affects their careers and quality of life.
Key Facts about Social Anxiety Disorder (Social Phobia)
Under-diagnosed as a Problem - It is estimated that about 20 million Americans are afflicted with it each year with this condition each year. It is rated as a common psychiatric disorder, being the third most common after alcohol abuse and depression. It is significantly under-diagnosed because many suffers are unaware that they have SAD and attribute it to general shyness and self-consciousness. Until recently it wasn't recognised as an affliction by the medical community and the general population and has probably not been diagnosed as it should.
Symptoms depend on cultural influences - The symptoms and expression of SAD depends on cultural background. In some Asian cultures such as Korea or Japan, people with SAD are more likely to offend others rather than being embarrassed. The specific disorders are also very dependent on cultural background.
Many SAD sufferers have other Problems and are Unaware of the Disorder - Many of those with SAD also suffer from depression and other personal problems such as addictions. Many males don’t realize they have social phobias and that they should seek help. The young age of onset, usually during the late teens or early twenties may affect recognition of the affliction and the need to seek help. It may be misdiagnosed as a related to the 'general 'dark teenager' years that are experienced by many young people.
SAD is classified as a phobia in a similar way that some people are afraid of snakes or heights or snakes - It is a phobia or fear about being in social situations. Its treatment is similar to that for other phobias.
It is related to genetics and environmental factors - SAD arises through of a combination of both environmental (circumstances) and biological (genetic) factors. Some individuals who are prone to it through inherited features may not develop SAD symptoms if their environment and circumstances does to lead to the triggers required for it to develop. Similarly someone may experience social incidents that cause embarrassment and feelings of inadequacy but not develop SAD if their genetics and personality are not prone for its development.
SAD is more than just shyness - The difference between shyness and SAD is that while many shy people feel uneasy in confronting situations, they do not feel fear in anticipation of future events, they don' have the severe physical symptoms and don't tend to actively avoid situations that make them shy and uneasy. Most shy people cope, while SAD people can't cope. Many people with SAD symptoms are not necessarily shy. They can be at ease with people and social situations most of the time, but a particular situation or trigger may give them intense feelings of anxiety that is unrelated to shyness.
SAD tends to go untreated and substantially undiagnosed - Studies have shown that most patients endure one or more of the symptoms for 10 years before seeking treatment. Only about one quarter of people with SAD symptoms get treatment. Social phobia by its very nature may make sufferers very reluctant to seek treatment, and sufferers and medical practitioners may discount it as simply bouts of shyness or normal social unease, especially in teenagers.
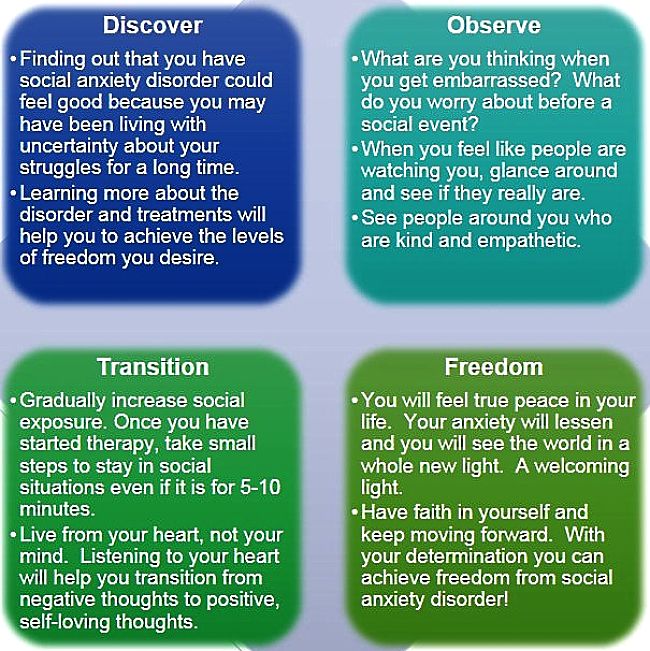
SAD is highly treatable! - People who suffer by themselves with the symptoms of SAD for a long time, may think that nothing can help and that nothing will change. However most sufferers who do seek and get treatment so show substantial improvement. A combination of various medications, and psychotherapy, singly or together have been shown to alleviate many of the symptoms.
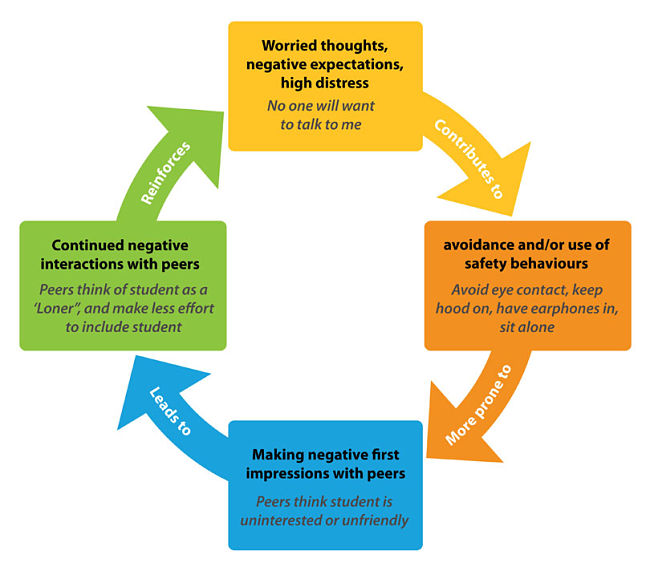
SAD is an expression of lack of self-confidence and can be magnified by being in the company of highly experienced people and unfamiliar situations and circumstances - SAD people become very self-conscious and take themselves very seriously - Sufferers tend to concentrate on every small problem they have in a social situation, and magnify them out of proportion to their actual affect on their interactions. One of more bad experiences tend to make things worse. Even blushing may trigger other symptoms as a sufferer imagines that all eyes are focused on them.
SAD can be Very Disruptive - Social phobia disrupts normal lives and interferes with careers and social relationships.
Many SAD people are aware of their problems but don't know how to fix them - Most people with social phobia are well aware that they have irrational and unjustified negative feelings are extreme and irrational. Yet the fear and dread still occurs and they may take all sort of evasive action to avoid it. Even when they manage to confront their fear, they may go through hell beforehand and feel very uncomfortable in dealing with it. Afterwards, their anxious feelings may persist, and they worry about how others may have judged them or their activities.
Specific Symptoms of Social Anxiety
Social anxiety disorder is characterized by the presence of all of the following symptoms:
-
A significant and persistent fear of one or more social or performance situations in which the person is exposed to unfamiliar people or to possible scrutiny by others. The individual fears that he or she will act in a way (or show anxiety symptoms) that will be humiliating or embarrassing.
Note: In children, there must be evidence of the capacity for age-appropriate social relationships with familiar people and the anxiety must occur in peer settings, not just in interactions with adults.
-
Exposure to the feared social situation almost invariably provokes anxiety, which may take the form of a situationally bound or situationally predisposed Panic Attack.
Note: In children, the anxiety may be expressed by crying, tantrums, freezing, or shrinking from social situations with unfamiliar people.
-
The person recognizes that the fear is excessive or unreasonable.
Note: In children, this feature may be absent.
-
The feared social or performance situations are avoided or else are endured with intense anxiety or distress.
-
The avoidance, anxious anticipation, or distress in the feared social or performance situation(s) interferes significantly with the person's normal routine, occupational (academic) functioning, or social activities or relationships, or there is marked distress about having the phobia.
-
In individuals under age 18 years, the duration is at least 6 months.
-
The fear or avoidance is not due to the direct physiological effects of a substance (e.g., a drug of abuse, a medication) or a general medical condition and is not better accounted for by another mental disorder.
-
If a general medical condition or another mental disorder is present, the fear in the first criteria is unrelated to it, e.g., the fear is not of Stuttering, trembling in Parkinson's disease, or exhibiting abnormal eating behavior in Anorexia Nervosa or Bulimia Nervosa.
Common Triggers for Social Anxiety Disorder
-
Public speaking.
-
Eating in public.
-
Being interviewed by a stranger.
-
Writing in public.
-
Shopping.
-
Speaking with strangers.
-
Using the phone.
-
Attending social events (e.g., parties, concerts)
-
Using public restrooms.
-
Talking with important people or authority figures.
-
Crowds.
-
Doing any sort of activity where the person might be watched. i.e. sexual interaction, standing in a line, or working in a public area.
Physical Responses and Signs of Social Anxiety Disorder
-
Rapid heartbeat.
-
Involuntary twitching.
-
Shaky voice.
-
Dry mouth.
-
Sweating.
-
Muscle tension.
-
Twitching.
-
Upset stomach.
-
Confusion.
-
Trembling or shaking.
-
Blushing.
Treatments
The treatments for SAD depend on whether it is a general or specific type of disorder and on the on the severity of the physical or emotional symptoms. Professional help should be sought for severe and debilitating cases. Generally, medication and therapy, and various combinations have been shown to be effective in treating SAD. Like many phobias, therapy by itself has been very effective in treating specific SAD. The main treatments for SAD are summarized below:
Medications for Social Anxiety Disorder - Various types of medication are prescribed to treat SAD. Each has its disadvantages and advantages depending on particular situation and person involved. Consult a medical practitioner regarding medical treatments.
Therapies
Cognitive-Behavioral Therapy (CBT) is a type of psychotherapy treatment designed to modify thought processes and behavioral responses to enhance positive emotions to various situations. The major techniques that have been shown to help are:
-
Exposure - Exposure can take place either through imagining the specific performance or social situation, or in-vivo.The underlying principle of exposure therapy is that through practice and experience, you will become more comfortable in situations that you would otherwise avoid. This is similar to many other phobia treatments, for example phobias to spiders.
-
Cognitive Restructuring - Cognitive restructuring focuses on the cognitive symptoms of SAD: poor self-concept, fear of negative evaluation by others, and negative attribution bias (attributing positive outcomes to chance and negative outcomes to your own shortcomings). It involves a series of exercises designed to identify negative thoughts, evaluate how true they are, and construct alternative thoughts to challenge the original thoughts.
-
Social Skills Training - Social skills training involves various exercises such as modeling, rehearsal and role-playing designed to help people learn appropriate behaviors and decrease anxiety in social situations. For example: conversations, eye contact, assertiveness and answering telephone calls
Psychodynamic Therapy - attempts to elicit the deeper unresolved reason for their anxieties. This may relate to childhood experiences and various set back that may have occurred. It also explores potential resistance to change.
Alternative Treatments - Alternative treatments for SAD include such things as dietary supplements, aromatherapy, and hypnotherapy.
Related Articles
=> Cyberchondria - How Online Search for Symptoms Triggers Anxiety
=> Home Remedies Panic Attacks - Symptoms and Treatments for Anxiety